Antibodies at your pipette tips
抗体是必不可少的在我们方面ne system to fight against all sorts of diseases that we could encounter every day. The technological developments over the decade has allowed scientist to isolate target or disease-specific antibodies in the laboratory without the need of animals or humans.

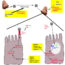
Fig. 1. Schematic shows the process for antibody phage display using the MSIA Streptavidin D.A.R.T’s.
A bacteria viral display system or phage display system has been widely used since last two decades to display peptides or proteins on the surface of the virus without disrupting the viral survival or replication processes. This virus is capable of displaying billions of antibodies on its surface via molecular cloning processes resulting in a collection of different antibodies. This collection is coined as an antibody library. This antibody library repertoire is of same diversity with the human body, thus allowing the library to be a reflection of the human immune repertoire. Antibodies are useful proteins found in the immune system to wade of infections and diseases. The specificity of antibodies to identify target specific proteins makes it an ideal tool for disease diagnostic and therapeutics.
In order to isolate antibodies from the library, an enrichment process has to be carried out. This involves the biopanning process where target specific antibodies are concentrated by virtue of physical binding between the antibody and the target protein. The biopanning process basically amplifies those specific binders and removes non-specfic ones, and from the pool of isolated binders, single clone identities are determined in random. The theory is similar to finding a needle in a haystack. Deviating from conventional methods to carry out biopaning, we introduce the use of an electronic multichannel pippete incorporating a special pitpette tip (MSIATMStreptavidin D.A.R.T’s®) to facilitate a semi-automated process for biopanning. Figure 1 shows the process involved in antibody phage display paning using the proposed system.
The method makes use of he similar concept of allowing the target molecules to be physically attached to a surface making it accessible to the antibody molecules passing through the tip. During this stage, the antibodies that are specific will bind to the mounted targets. This allows for physical isolation of the specific and non-specific antibodies from the pool. The attached antibodies that are still physically connected to the phage particle, is then removed by acid elution. The eluted phages are then rescued for downstream identification.
In conclusion, a modified biopanning method using the MSIATMStreptavidin D.A.R.T’s®provides an interesting alternative to identify antibodies via phage display in a semi-automated fashion.
Theam Soon Lim
Institute for Research in Molecular Medicine, University Sains Malaysia,
Penang, Malaysia.
Publication
Application of streptavidin mass spectrometric immunoassay tips for immunoaffinity based antibody phage display panning.
Chin CF, Ler LW, Choong YS, Ong EB, Ismail A, Tye GJ, Lim TS.
J Microbiol Methods. 2016 Jan












Leave a Reply
You must belogged into post a comment.