Advantages of using pectoralis major fascia in rhinoplasty
Fascia is frequently used in rhinoplasty, both in primary cases and in revision rhinoplasty cases. There are several reasons for using fascia in rhinoplasty: fascia is resistant to infection, has a good survival rate, and is easy to shape yet strong enough to be sutured.

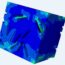
Fig. 1. The superficial surface of the pectoralis major fascia may be exposed by elevating the adjacent subcutaneous tissues (left on the picture: cephalic).
In primary rhinoplasty cases fascia may be used as a cover blanket over the nasal osteocartilaginous framework to prevent any irregularity to become apparent, especially in thin skin patients. Fascia may also be layered to slightly augment the nasal dorsum or to increase tip definition. In revision rhinoplasty cases temporalis fascia can be particularly useful to camouflage any irregularity of the bony or cartilaginous nasal framework. Temporalis fascia may also be used in patients requiring major augmentation of the nasal dorsum or in saddle nose patients, as the outer layer and container of diced cartilage.
The deep temporalis fascia is most frequently used in rhinoplasty. Harvesting this fascia requires a straightforward surgical technique and the resulting scar is hidden by hair. Nevertheless, a second surgical incision in a separate surgical field is necessary for harvesting this fascia, adding surgical time to the rhinoplasty procedure and morbidity to the patient.
In patients requiring autologous costal cartilage, as frequently occurs in augmentation rhinoplasty cases and in revision rhinoplasty cases, and if costal cartilage is taken from the 5thto the 7thribs, pectoralis major fascia is directly in the surgical field for rib harvest and has to be incised to provide access to the thoracic grid. Harvesting this fascia at this stage of the surgery is straightforward.

Fig. 2. The deep surface of the pectoralis major fascia may be bluntly elevated form the underlying muscle after incising the fascia (left on the picture: cephalic).
Pectoralis major fascia covers all the surface of the pectoralis major muscle and is, therefore, abundant. It is thin and elastic but also strong, sharing many physical and histological characteristics with the deep temporalis fascia. It has, therefore, ideal features to be used in the nose, just as much as the deep temporalis fascia. Pectoralis major fascia may be used over the bony and cartilaginous nasal framework to prevent any irregularity to become apparent, may be layered over the nasal dorsum to induce a slight dorsal augmentation, may be layered over the nasal tip to slightly increase tip definition and projection and may be sutured to be used as the outer layer of diced cartilage.
我们已经经常收获一块pectoralis major fascia whenever autologous costal cartilage is to be used for rhinoplasty. In this way, a piece of fascia of the necessary size is obtained and a second surgical incision in the temporal region is avoided, as is the inherent morbidity associated with another surgical field. We have experienced no local complications such as local seroma formation or muscle dehiscence, in line with other kind of surgeries in which the pectoralis major fascia is also elevated from the pectoralis muscle. This fascia is routinely elevated and removed during radical mastectomy and no measures to prevent muscular dehiscence need to be taken. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that the removal of pectoralis major fascia during mastectomy has no influence on the amount of bleeding during surgery or on the postoperative formation of seroma.
In breast augmentation surgery the pectoralis major fascia is frequently elevated from the underlying muscle to create a potential space external to the pectoralis major muscle where the implant is introduced. Pectoralis major fascia may also be harvested and used as a free graft to repair dura mater defects in neurosurgical procedures.
Harvesting and using pectoralis major fascia in rhinoplasty cases requiring autologous costal cartilage precludes the need for a separate surgical field adding extra surgical time to the procedure and extra morbidity to the patient. Pectoralis major fascia may be an alternative source of fascia for rhinoplasty.
Rui Xavier
Hospital da Arrabida
Porto, Portugal
Publication
胸大肌筋膜在鼻整形术。
Xavier R.
Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2015 Jun











Leave a Reply
You must belogged into post a comment.