Dental fillings with anti-inflammatory effect
牙疼是由深龋病变和提升crown fractures. It occurs due to an inflammatory process in pulp tissue, which is the vascularized and innervated tissue in the most internal portion of tooth. Early and conservative dental treatments prevent the evolution of the pulp inflammation and can avoid root canal intervention. For the conservative treatments, dentists remove minimal portion of dentine (the middle tissue of tooth) and fill cavity with resin material. The first layer in the deepest portion of cavity is a fluid resin, called adhesive resin. However, the current materials to fill tooth have no anti-inflammatory properties and do not improve long-term success rate. Besides, the systematic anti-inflammatory drugs presents limited effect in pulp tissue and can promote adverse effects in gastrointestinal tissues.

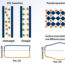
Fig. 1. Tooth before and after treatment. A) Tooth with a deep carious lesion and an injured pulp tissue. B) Tooth filled with adhesive resin containing nanocapsules with indomethacin; indomethacin is released from resin to pulp tissue (gray arrows); health pulp tissue.
To improve drugs effect and decrease toxicity, nanoparticles have been received considerable attention over the last few years. Nanoparticles works as a carrier system to promote a specific distribution of drugs, leading to high concentration in target sites. Polymeric nanocapsules that contain drugs promote controlled drug release (slow release in long-term), improving bioavailability, efficacy and adverse effects reduction.
In our study, we used indomethacin, an anti-inflammatory drug, which inhibits the processes of inflammatory and sensory responses through the block of signals. With the aim of improving the local efficacy of anti-inflammatory action in tooth through controlled drug release, we formulated an adhesive resin for restoration with nanocapsules containing indomethacin. The nanocapsules had a medium size of 165 nm, which corresponds to ten times lower than a blood cell.
Our adhesive resin demonstrated good performance to fill tooth with controlled release of indomethacin. Besides, the indomethacin released from resin is able to penetrate the tooth, achieving the pulp tissue without any toxicity to human body.
Our satisfactory results indicate that the adhesive resin with nanocapsules containing indomethacin may protect pulp tissue when there is a deep cavity in tooth. Then, it is a good alternative instead of the currently used materials to improve long-term success rate.
Fabricio Mezzomo Collares
Dental Materials Laboratory, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul,
Ramiro Barcelos Street, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
Publication
Effect of indomethacin-loaded nanocapsules incorporation in a dentin adhesive resin.
Genari B, Leitune VC, Jornada DS, Camassola M, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS, Samuel SM, Collares FM
Clin Oral Investig. 2016 Apr 12











Leave a Reply
You must belogged into post a comment.